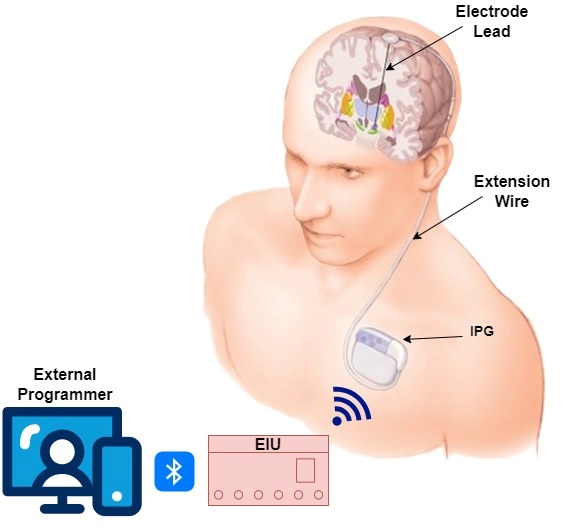
Common neurological disorders of the brain that affect motor function and coordination of body movement include Parkinson’s disease, dystonia and essential tremor. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is used to treat these neurological conditions; in addition, it shows promise in the treatment of epilepsy, obsessive compulsive disorder and depression. DBS technique involves implanting electrodes in specific areas of the brain and delivering carefully controlled electrical stimulation to these precisely targeted areas of the brain responsible for motor function of respective brain disorder. Functional electrical stimulation provides an alternative therapy in the treatment, although it is normally used in addition to medication. By delivering an electrical stimulus to parts of the brain responsible for motor function, control of muscle movement is achieved by blocking neural signals which cause symptoms associated with the disease. Areas of the brain targeted for electrical stimulation include the sub thalamic nucleus or the globuspallidusinterna. Electrodes are placed on both sides of the brain for bilateral stimulation of these areas. The amount of stimulation is provided and controlled by a pacemaker-like electronic device, known as Implantable Pulse Generator (IPG), placed under the skin in upper chest. A wire that travels under the skin connects this device to the electrodes in the brain. The parameters of stimulation are set by an external programmer, either by a clinician or the patient.
Common neurological disorders of the brain that affect motor function and coordination of body movement include Parkinson’s disease, dystonia and essential tremor. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is used to treat these neurological conditions; in addition, it shows promise in the treatment of epilepsy, obsessive compulsive disorder and depression. DBS technique involves implanting electrodes in specific areas of the brain and delivering carefully controlled electrical stimulation to these precisely targeted areas of the brain responsible for motor function of respective brain disorder. Functional electrical stimulation provides an alternative therapy in the treatment, although it is normally used in addition to medication. By delivering an electrical stimulus to parts of the brain responsible for motor function, control of muscle movement is achieved by blocking neural signals which cause symptoms associated with the disease. Areas of the brain targeted for electrical stimulation include the sub thalamic nucleus or the globuspallidusinterna. Electrodes are placed on both sides of the brain for bilateral stimulation of these areas. The amount of stimulation is provided and controlled by a pacemaker-like electronic device, known as Implantable Pulse Generator (IPG), placed under the skin in upper chest. A wire that travels under the skin connects this device to the electrodes in the brain. The parameters of stimulation are set by an external programmer, either by a clinician or the patient.
DBS SYSTEM COMPONENTS
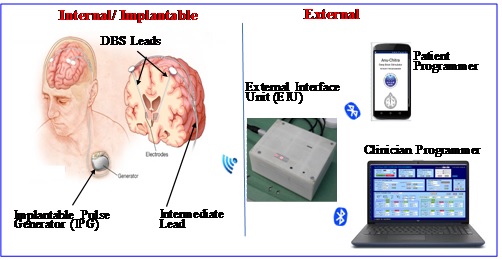
The Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) system consists of implantable components viz. Implantable Pulse Generator (IPG), electrode/brain lead & intermediate lead and external components viz. External Interface Unit (EIU), Patient Programmer (PP) & Clinician Programmer (CP). The IPG is implanted subcutaneously in the sub-clavicular or upper abdominal region. It is comprised of a battery and integrated circuits that are hermetically sealed in titanium enclosure. Two leads having four electrodes each are implanted in two hemispheres of the brain for bilateral stimulation. Non-invasive adjustment of the stimulation parameters and wireless charging of IPG battery are achieved using the external components of the DBS. CP is used by clinician/doctor for complete control while the PP is used by patient for status check and limited control of therapy parameters.
INTRODUCTION
Common neurological disorders of the brain that affect motor function and coordination of body movement include Parkinson’s disease, dystonia and essential tremor. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is used to treat these neurological conditions; in addition, it shows promise in the treatment of epilepsy, obsessive compulsive disorder and depression. DBS technique involves implanting electrodes in specific areas of the brain and delivering carefully controlled electrical stimulation to these precisely targeted areas of the brain responsible for motor function of respective brain disorder. Functional electrical stimulation provides an alternative therapy in the treatment, although it is normally used in addition to medication. By delivering an electrical stimulus to parts of the brain responsible for motor function, control of muscle movement is achieved by blocking neural signals which cause symptoms associated with the disease. Areas of the brain targeted for electrical stimulation include the sub thalamic nucleus or the globuspallidusinterna. Electrodes are placed on both sides of the brain for bilateral stimulation of these areas. The amount of stimulation is provided and controlled by a pacemaker-like electronic device, known as Implantable Pulse Generator (IPG), placed under the skin in upper chest. A wire that travels under the skin connects this device to the electrodes in the brain. The parameters of stimulation are set by an external programmer, either by a clinician or the patient.
DBS SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) system consists of implantable components viz. Implantable Pulse Generator (IPG), electrode/brain lead & intermediate lead and external components viz. External Interface Unit (EIU), Patient Programmer (PP) & Clinician Programmer (CP). The IPG is implanted subcutaneously in the sub-clavicular or upper abdominal region. It is comprised of a battery and integrated circuits that are hermetically sealed in titanium enclosure. Two leads having four electrodes each are implanted in two hemispheres of the brain for bilateral stimulation. Non-invasive adjustment of the stimulation parameters and wireless charging of IPG battery are achieved using the external components of the DBS. CP is used by clinician/doctor for complete control while the PP is used by patient for status check and limited control of therapy parameters.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
| Sr. No. | Specification | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stimulation | Bilateral (two leads with 4 electrodes each) |
| 2 | Electrode Lead | Platinum Iridium (Pt-Ir) alloy based inline quadrifilar cable, having four Pt-Ir ring electrodes with inter-electrode gap. |
| 3 | Implantable Pulse generator | Programmable features, Titanium Grade-5 enclosure, working life >10 years, weight <50g, volume <40cc |
| 4 | IPG Programmable parameters | Pulse Amplitude (0-10v/0-25mA), Width (30-450us), Repetition Frequency (2-250Hz), Mode (Current/Voltage), Type (Monopolar/Bipolar), user selection of Lead and Electrodes etc. |
| 5 | EIU interfaces CP/PP to the IPG and facilitates wireless charging | |
| 6 | Wireless communication with IPG, on the LF band, for parameters’ setting and status check | |
| 7 | Proprietary wireless charging of IPG battery through Titanium casing | |
| 8 | Patient Programmer (PP) Android App to control therapy parameters, within the limits set by the clinician | |
| 9 | Clinician Programmer (CP) application software for complete control by a doctor | |
| 10 | Bluetooth link between EIU and PP/CP | |
Machinery and Space
MAN POWER
Test Equipment
The DBS technology has been developed, few prototypes have been evaluated for functional requirements and safety considerations and found to meet desired specifications. The DBS technology is being offered on as is where is basis. Preclinical and Clinical Evaluation including the Pilot production, Regulatory Clearance, qualification testing as per the applicable standards, documentation, software V&V etc. shall be responsibility of the technology licensee.