

Curcumin is the major active ingredient in turmeric which is known in India as a medicinal herb since ancient times. It is known to possess excellent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic and anti-arthritic activities. Curcumin has been found to be safe and nontoxic for humans. The following four formulations are available for transfer of technologies-
Curcumin is the major active ingredient in turmeric which is known in India as a medicinal herb since ancient times. It is known to possess excellent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic and anti-arthritic activities. Four different formulations have been developed with curcumin as a key ingredient.
Curcumin is the major active ingredient in turmeric (Curcuma longa) rhizome which is known in India as a medicinal herb since ancient times. It is a hydrophobic polyphenol, with a variety of pharmacological properties. It is one of the highly researched molecules with excellent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic and anti-arthritic activities. Curcumin has been found to be safe and nontoxic for humans, even in grams quantities. In spite of such excellent properties, there is a limitation in its application due to poor bioavailability and aqueous solubility. To overcome these problems, several new formulations based on natural proteins, amphiphiles and carbohydrates are prepared that have ability to improve water solubility and work as efficient delivery vehicle of curcumin. These formulations would find application in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, functional food and other related areas. A few formulations for which technical know-how has been developed are illustrated in brief.
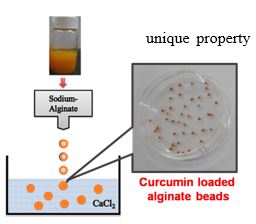
Alginate is a carbohydrate based polymer, having of forming gels in presence of specific metal ions. During the gelation process, hydrophobic cavities are created that can efficiently trap curcumin. Using special laboratory methods the curcumin loaded gels can be converted to uniformly loaded spheres of size ranging from micron to nanometers. These curcumin loaded beads can be used directly or in association with other excipients in the nutraceutical formulation. Around 80-100 mg of curcumin loading is achieved per gram of dry beads.

Gelatin is an animal protein formed by partial hydrolysis of collagen, with a long history of safe use in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, as well as food products thus being considered a GRAS material by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Using novel physical laboratory methods, a nano gelatin formulation of size < 150 nm has been prepared that provide hydrophobic pockets to trap curcumin. These nanogels can be used as lyophilized powders, lozenges or pastilles. Once dissolved in water they release bioavailable liposomal curcumin. Approximately 30 mg of curcumin can be loaded per gram of gelatin.

PEG coated vesicles (liposomes) are important vehicles for the passive targeting of anticancer drugs. PEGylated liposomes were prepared using co-assembly of biocompatible and cost effective ingredients. The structure of the aggregates can be tuned from micelles to rod-like micelles or vesicles and size can be controlled from 50 to 300 nm. About 22 mg of curcumin can be loaded per gram of the excipients. The developed formulation show pH dependant sustained release of curcumin from PEGylated liposome. The product can be reconstituted for pharmaceutical applications.

Nasal drop formulations of curcumin were prepared using biocompatible amphiphiles with size less than 50nm. Curcumin loading efficiency of 50mg/ml has been achieved in the formulation. The concentrate can be diluted to any extent without phase separation or leaching out of the active ingredient. The intranasal pathway is a non-invasive alternative to bypass blood-brain barrier and limit systemic side effects. The optical clarity of the formulation is advantageous for ocular delivery as well.
RAW MATERIALS
Major Equipments for large scale production
SPACE
POWER
MANPOWER
